Table of Contents
What is Hiatus Hernia?
Our chest and abdomen are separated by a muscular organ known as the diaphragm. It contains a hole which is called hiatus from which the lower end of the esophagus passes to open into the stomach. So this disorder is named hiatus hernia.
It is the condition in which the stomach protrudes or bulges above the diaphragm through this hiatus.
What causes hiatus hernia?
The exact cause is not clear but various factors affect the disorder such as…
- Age: It is most common in middle-aged people especially in females with obesity. It may also be congenital in that the hiatus opening may be larger than it should be.
- The conditions which can raise intra-abdominal pressure like pregnancy, obesity, ascites, or tumors in the abdomen may be predisposing factors to develop it
- It may be caused after surgical procedures like partial gastrectomy or vagotomy.
- Injury in that particular area may also develop it.
Types
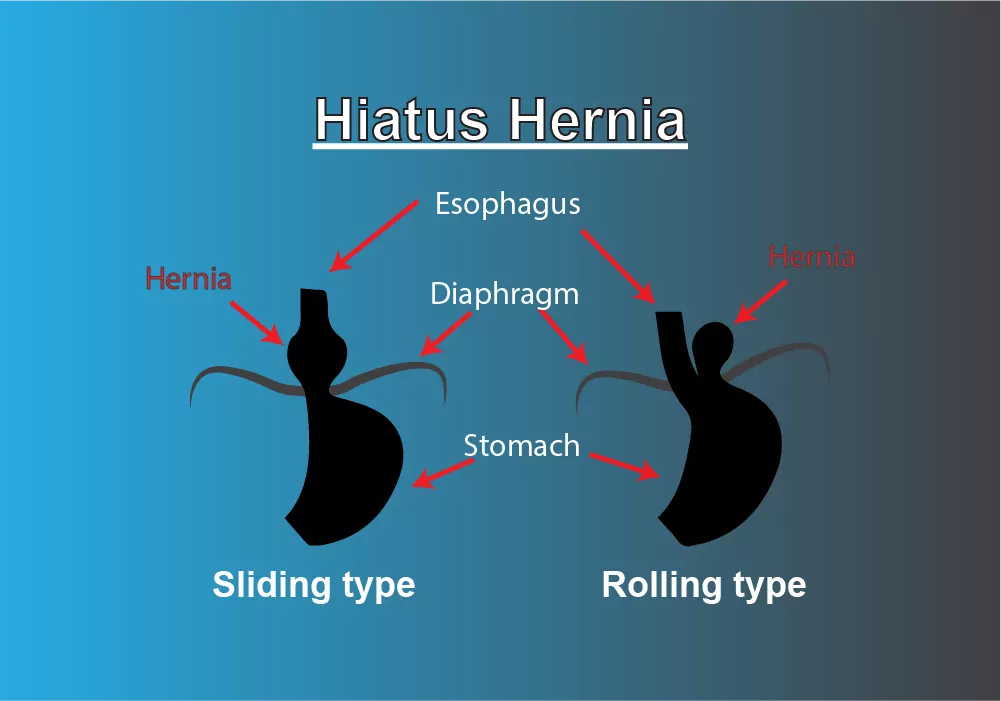
There are two types of hiatus hernia. One is sliding and the other is rolling.
Sliding hernia:
It is the most common type in which simple protrusion or upward sliding of the stomach with an esophagogastric junction or lower esophageal sphincter or part through the hiatus into the chest.
Rolling hernia:
It is also called a para esophageal hernia.
In this type esophagogastric junction is within the abdominal cavity but some part of the gastric fundus bulges upward through the hiatus into the thoracic cavity.
Sometimes this type of hernia can be dangerous because it blocks the blood supply due to a squeezed part of the stomach. It is called a strangulated hernia and urgent surgical intervention may be needed in these cases.
Symptoms
Symptoms due to Acid Reflux:
Hiatus hernia is one of the causes of GERD and due to this following symptoms can be present in the patient
- Heartburn or regurgitation of the gastric content or food especially on stooping or bending forward
- There may be respiratory choking attacks and aspiration pneumonia due to regurgitation, especially at night.
- Chest pain or discomfort behind the sternum especially on lying down or stooping immediately after meals.
- In the case of esophageal muscle spasms or esophagitis, there may be dysphagia.
Symptoms due to pressure:
- Dilated esophagus or herniated gastric pouch may cause pressure on the mediastinum which presents symptoms like dyspnea, cough, palpitation, or anginal pain.
- It can also put pressure on the diaphragm causing symptoms like spasmodic pain or hiccup.
Symptoms due to hemorrhage:
- Esophageal ulcer may develop due to hiatus hernia causing iron deficiency anemia from the massive hematemesis or oozing from the ulcer.
Symptoms due to associated diseases
- Abdominal discomfort or pain is thereby many other associated diseases like peptic ulcer, cholecystitis, or ischemic heart disease.
Complications
- A strangulated hernia is the most common complication of a rolling hiatus hernia and an emergency surgical operation may require in this case.
- Esophageal ulcer may develop and due to which anemia is the common complication from the hemorrhage.
Diagnosis
Radiological investigations
- X-ray chest: There may be retro-cardiac shadow with fluid level when a sliding hernia is large.
- Barium swallow: Barium is swallowed and multiple x-rays are taken to evaluate the size of the hernia and any other complications or conditions.
- CT scan of abdomen: is also helpful to find out it.
Endoscopy:
It is a very important investigation and also finds out complications if any. It’s also helpful to take a biopsy whenever necessary.
Manometry:
Sometimes barium meal investigation may be presented normally. In this case, manometry is a very sensitive method in the absence of dilatation of the esophagus.
Treatment
(A) Medical:
To control gastro-oesophageal reflux following medicines can be given.
- Proton pump inhibitors like omeprazole, rabeprazole, pantoprazole, lansoprazole.
- H2 blockers like ranitidine, famotidine, or cimetidine reduce gastric acidity and pepsin secretion.
- Antacid which protects against damage to the gastric and esophageal mucous membrane from stomach acids.
(B) Surgical:
- Emergency surgical procedure in case of strangulated hernia develops.
- Laparoscopic surgical operation to reduce larger hiatus opening. Laparoscopic surgical procedure is minimal invisible and have small cuts on the skin, lesser chances of postoperative infection, less pain and scarring, and patient recovers fast than traditional open abdominal surgeries.
(C) Lifestyle change and home remedies:
- Elevate the bed head by 20cm.
- Avoiding postural precipitating reflux which is caused by stooping forward or sitting in a low chair.
- Avoid large meals.
- Avoid food or drinking before 3 to 4 hours of bedtime and also avoid exercise or lying down immediately or 3 to 4 hours after food.
- Losing weight is very important if the patient is obese.
- Avoid taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine whenever possible.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol.
- Avoid foods that can trigger symptoms like pastries, coffee, fatty foods, vinegar, chocolate, caffeinated drinks, and acidic fruits like sweet lime or mosambi in excessive quantity, etc.
- Avoid tight clothing that can cause pressure on the abdomen.
Hiatus Hernia FAQs
Can a hiatus hernia be cured?
Hiatus hernia doesn’t go away by itself. The symptoms can be controlled by medicine and the condition is much better managed by surgery. So laparoscopic surgical repair of the hernia is the main treatment and cure for it. It has many positive results and improvements in the quality of life.
Is hiatus hernia hereditary?
No sure evidence is there that suggests its hereditary connection. But it can be congenital in that there is a larger hiatus opening than usual in the diaphragm from childhood.
Does a hiatus hernia cause bloat?
Yes, it can. It is mainly due to gastroesophageal reflux disorder in which gastric acid irritates the esophagus. Abdominal discomfort like bloating and heartburn are common in this condition. Please also read the symptoms section above for more details.
Can a hiatus hernia cause back pain?
Usually, pain and other symptoms in a hiatus hernia are due to acid reflux in the esophagus and pressure on the surrounding area. Back pain, especially in the middle of the back, is usually not present in this condition but it depends on other associated conditions also, which can refer pain to in the back. And due to this patient may have stiffness or tightness of muscles of the back.
Where the pain of the hiatus hernia is located?
Many patients with hiatus hernia are asymptomatic. They get diagnosed with the condition during routine investigations of other diseases. Symptoms in the cases are due to gastric acid reflux or pressure on the surrounding organ or area.
Gastroesophageal Reflux symptoms are heartburn, regurgitation, dyspnea, and unusual feeling in the throat. It can also irritate the esophagus causing chest pain which is mostly located behind the sternum or breastbone.
In a hiatus hernia, there may be pressure on the mediastinum causing anginal pain, and palpitation in the lower chest area.
Pressure on the diaphragm irritates it causing hiccups and spasmodic pain mainly in the epigastric region.
What type of history is taken from the patient of hiatal hernia?
All the necessary history and evaluation of the patient should be done to diagnose hiatal hernia and other associated conditions.
Age should be asked as it is more common in older ages. It can also be congenital.
Any history of injury on the abdomen or area where hiatus in the diaphragm is located should be evaluated.
Past history of any disease that can cause an increase in intra abdominal pressure like obesity, ascites, or mass in the abdomen. Because increased intra-abdominal pressure is one of the predisposing factors to developing a hernia. Also, take a history of ongoing pregnancy as it increases the intra-abdominal pressure.
Past history of any abdominal surgical procedure like vagotomy or gastrectomy should be evaluated as it may develop hernia mostly due to weakened muscle.
Can I play sports like football if I have a hiatus hernia?
It depends on clinical findings and how serious your condition is. The exercises or sports which can put more strains on the diaphragm and abdominal muscle can increase the condition of hiatus hernia. Usually walking and jogging are suitable exercises over running in cases of hernia. So football is the sport where you need more running and it can cause strain on abdominal muscles and diaphragm.
Exercise like swimming, cycling, walking, jogging, and gentle yoga are advised rather than heavy exercise with too much running, situps, deadlifting, weight lifting, push-ups, and yoga which has inversion body poses.
Can hiatus hernia and anterior abdominal hernia operations be made simultaneously?
Hiatus hernia and anterior abdominal hernia like umbilical hernia or hernia developed by any post-operative procedures of the abdomen are usually surgically corrected. If multiple hernia is there then also it can also be surgically operated on if the condition of the patient is suitable.
The outcome of the surgery is usually very good. It depends on many factors. But it is possible except for high-risk cases. Your treating doctor will decide what to do. You can read more detail on the laparoscopic treatment of hernia here.